Basic principles to avoid spam that engineers should know
Learn how the junk e-mail filter can determine junk e-mail so that information for users can be delivered properly without being blocked.
How the junk mail filter works: For Gmail
It seems that the grounds for judging junk mail in Gmail are published to some extent by Google.
Email address spoofing Phishing scam Emails from unconfirmed senders Policy set by the administrator Blocking emails from specific senders Email with empty content E-mail manually sorted into junk e-mail
Source: Marking and unmarking junk mail-PC-Gmail Help https://support.google.com/mail/answer/1366858
From the above, I will pick up and explain some reasons.
Email address spoofing
The email address is very similar to the existing sender's address. This is the case when the alphabet "O" in the email address is the number "0".
Emails from unconfirmed senders
This item is very important. One of the characteristics of spam mail is that it rewrites the header information of the sender and sends it.
When sending and receiving mail between servers, a protocol called SMTP is used. One of the security weaknesses of SMTP is the ability to impersonate the sender of any domain.
Now let's see how it works to see how it can be spoofed.
Email structure
Email consists of three main parts:
- Envelope
- Message Header
- Message Body
Source: How email spoofing works and why spoofing is so easy | Proofpoint JP https://www.proofpoint.com/jp/corporate-blog/post/how-does-email-spoofing-work-and-why-it-so-easy
The source address is specified in the Envelope and Message Header. The respective source addresses are called Envelope From and Header From.
HeaderFrom can be freely rewritten by the sender. Since HeaderFrom is displayed on the mailer, it can be disguised as an email sent from a legitimate domain.
Since Envelope is destroyed when it reaches the Inbox, it seems difficult for the receiving user to check the Envelope information on the mailer (under investigation).
From the above structure, it is necessary to have a mechanism to guarantee that the source address is appropriate.
SPF
Abbreviation for Sender Policy Framework. Authenticate the source using an SPF record, which is a type of DNS TXT record.
The incoming mail server queries the DNS of the source domain for the information contained in EnvelopeFrom to verify the source.
Operation image diagram:
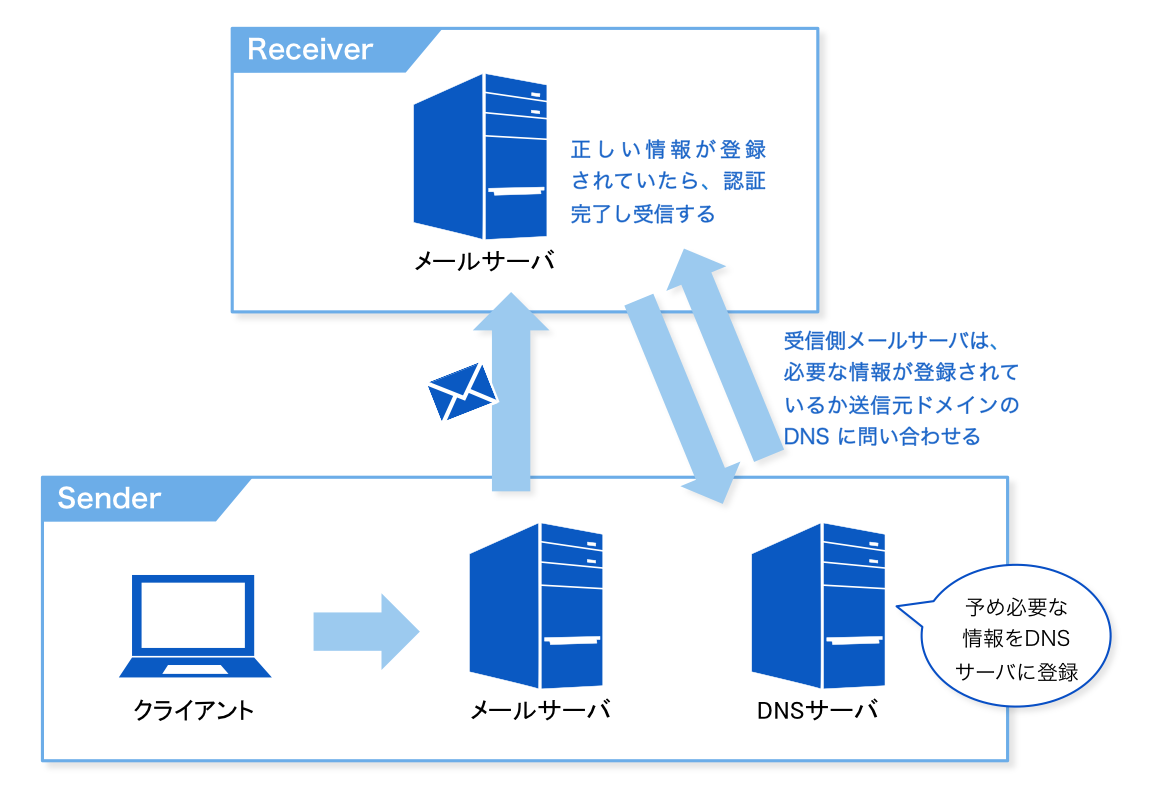
(Source: Get to know SPF records for authenticating senders | SendGrid Blog)
You can set it yourself, but if you use SaaS for sending emails, it will be set automatically in many cases.
Summary
--It's easy to disguise the sender of an email --SPF is one of the mechanisms to verify the source address --If SPF is registered in DNS, it is often judged to be a legitimate source.