Simplified Path input when enabling virtual environment in venv
0. Overview
In this article, when enabling a virtual environment using venv on the command prompt, By using command macros, we have summarized how to simplify complicated command input.
↓ This is
C:\users\username\envs\hogeenvs\Scripts\activate.bat
↓ It will be like this.
ahogeenvs
1. Background
I was not satisfied with Anaconda and decided to reorganize the Python development environment. So I uninstalled Anaconda, simply installed Python, and started to improve the environment.
2. Environment
PC:Windows10 Enterprise 1809 System: 64bit Terminal: Use command prompt (hereafter, cmd)
3. Trouble
Activation of virtual environment, which was easy to execute with conda, In venv, I had to enter complicated commands.
For example, let C: users / username / envs be the folder containing the virtual environment information. It is assumed that the usual work environment folder is set up in a different location.
So if you want to enable the virtual environment "hogeenvs" With conda, it was not necessary to enter the path to the virtual environment, so
activate hogeenvs (c1)
I should have described it as. However, venv requires the path from the current folder to the virtual environment folder, so
C:\users\username\envs\hogeenvs\Scripts\activate.bat (c2)
Must be stated.
This problem,
- Make the virtual environment information folder and the work environment folder the same, and enter them with a short relative path.
- Raise the hierarchy of the folder to be used as high as possible and enter it with a short absolute path.
Although it can be solved by this method, If that does not happen, you need to manually enter (c2) above.
4. Solution
4.1 Macro registration with doskey command
Use command macros (called aliases in the Linux environment). First, enter the following on cmd.
doskey ahogeenvs=C:\users\username\envs\hogeenvs\Scripts\activate.bat (c3)
As a result, if you type the command ahogeenvs on cmd after that, you will have entered the same command as in (c2).
Of course, ahogeenvs is an arbitrary command, and you can set your own favorite command.
However, if you give it a name that exactly matches the folder (in this case, `` `hogeenvs```),
Since there was a concern that a problem would occur when operating this folder itself, I set it as (c3).
4.2 Output the registered macro as a macro file
The macro set in 4.1 becomes invalid when cmd is closed. Therefore, output this as a macro file and use the methods of 4.3 and 4.4. It is necessary to make it available continuously in the future.
With the following command, the list of registered command macros is output to "c: (arbitrary path) \ cmd_macros.txt".
doskey /macros > c:(Arbitrary path)\cmd_macros.txt (c4)
4.3 Load macro file at startup
The file created in 4.2 is collectively registered as a command macro when the following command is entered when cmd is started.
doskey /macrofile=c:(3.Path set in 2)\cmd_macros.txt (c5)
Use the following command to check whether the settings are reflected.
doskey /macros (c6)
4.4 Macro file automatic reading setting when cmd is started
In the method of 4.3, it is necessary to input (c5) each time when cmd is started.
This is very complicated, so make sure that the command file is automatically read when cmd is started.
First, enter "cmd" from the search file and select "Open file location" from there.

Then, the cmd shortcut is displayed as shown above, so right-click it to open the properties. Put a half-width space after cmd.exe of "link destination (T)" (red circle in the lower left figure),
(Path information)\cmd_macros.Enter txt and click Apply.
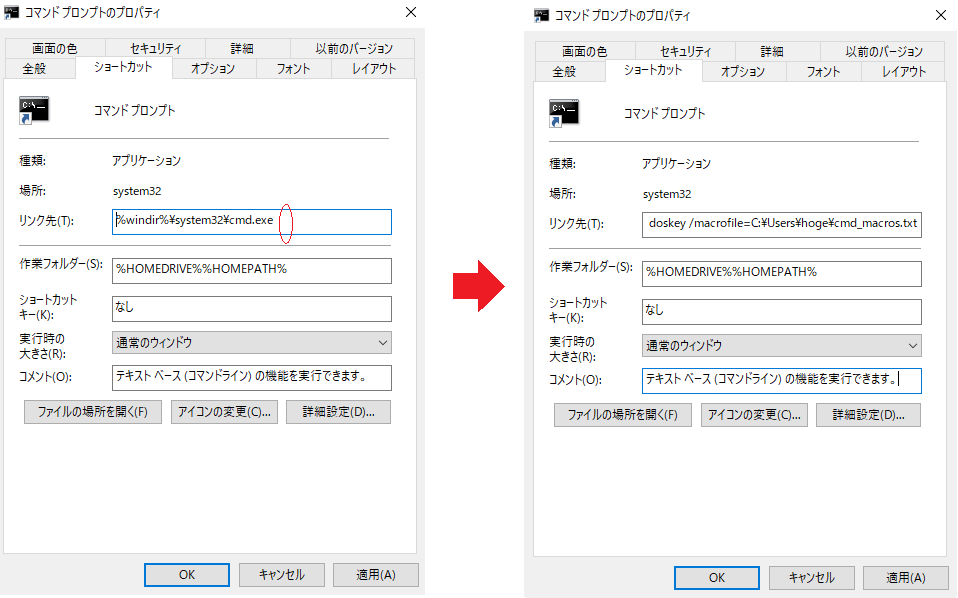
Now, the next time you start cmd, the macro file will be loaded automatically.
Note that <b> cmd is always started from this shortcut </ b>.
If you want to use different shortcuts, you need to set the same as 3.4 for each shortcut.
## Reference URL
Details about operations from 4.1 to 4.4.
<https://www.adminweb.jp/command/command/index2.html>
On the command prompt using command macros
When you want to operate commands like a Linux terminal.
<https://qiita.com/asmin/items/d53e71ed98a377ca7823>
<https://www.ilovex.co.jp/blog/system/windows/dos-ailias.html>
Recommended Posts