[JAVA] I tried to develop the cache function of Application Container Cloud Service in the local environment
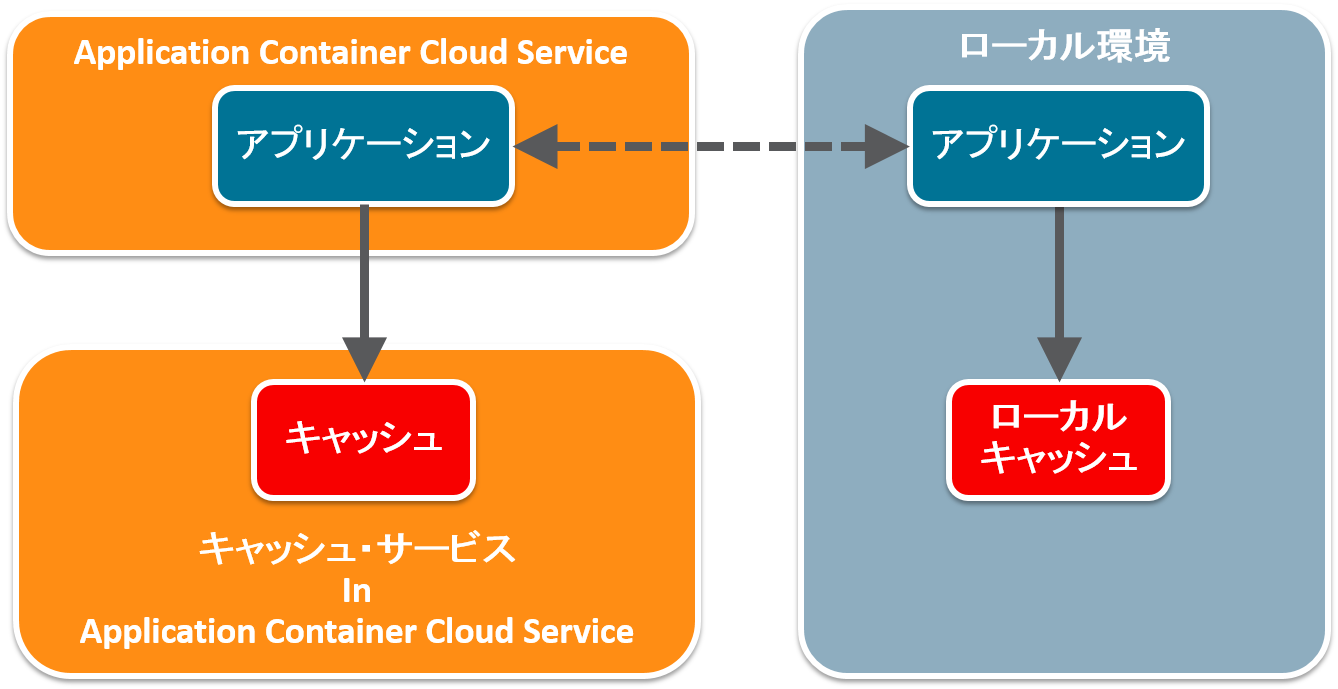
Oracle Application Container Cloud Service provides caching functionality.
-I tried using the cache function of Application Container Cloud Service
The ** Local Cache ** feature is available to facilitate the development of this cache feature.
Description
Application Cache provided by Oracle Application Container Cloud Service gets the name of the running host from the environment variable and uses it as the cache destination. Therefore, in order to use the cache function, it is a prerequisite that the Application Cache instance is created and started on the Application Container Cloud Service.
-Reference: Cache initialization
It is inconvenient to connect remotely during development for testing and debugging. Therefore, use the ** LocalCache ** API provided by the Application Cache Client.
LocalCache
LocalCache provides an API similar to the API when using Cache on the actual Application Container Cloud Service.
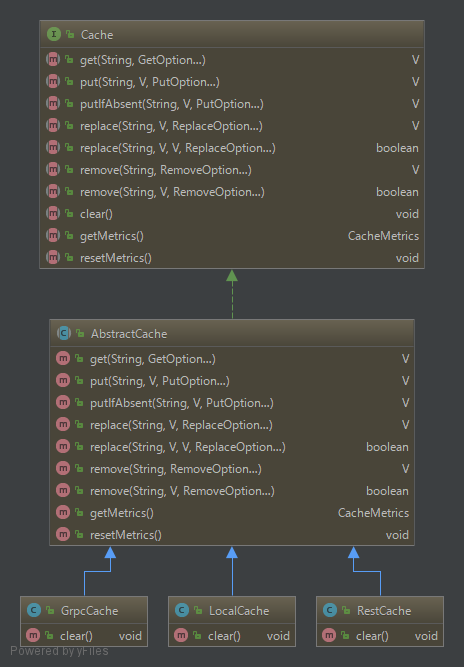
As you can see from the class diagram above, ** AbstractCache ** that implements the ** Cache interface ** inherits the abstract class for ** REST ** processing, ** gRPC ** processing, ** local * * Each class for processing is created.
RestCache / GrpcCahe
The cache created in "I tried using the cache function of Application Container Cloud Service" has a ** REST ** type in the ** Transport ** class. It was specified. It is therefore defined as ** RestCache **.
cacheSession = sessionProvider.createSession(Transport.rest());
Also, if you specify a Transport type of ** gRPC **, it will be defined as ** GrpcCache **.
function
There is no difference in the basic functions of LocalCache, RestCache, and GrpcCache.
--Get cache
get(String key)--Cache registrationput(String key, V value, PutOption... options)--Cache updatereplace(String key, V value, ReplaceOption... options)--Clear cacheremove(String key, RemoveOption... options)
Premise
The following libraries are required to use the Java API for the cache service client application.
- cache-client-api-1.0.0.jar
It can be obtained by describing the following dependency by Maven:
- Artifact ID: cache-client-api
- Group ID: com.oracle.cloud.caching
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle.cloud.caching</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-client-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
Usage / Implementation example
It is convenient to switch the Cache used when running on Application Container Cloud Service and when running in a local environment. Therefore, let's use environment variables as identification information on Application Container Cloud Service or local environment.
In Application Container Cloud Servive, the directory name is registered in the environment variable ** APP_HOME ** as the information of the location where the deployed application file is placed. Therefore, we will use the presence or absence of this environment variable to determine the environment difference.
Before inserting the environment discrimination process
Session cacheSession = new RemoteSessionProvider(CACHE_URL).createSession(Transport.rest());
Cache cache = cacheSession.getCache(CACHE_NAME, ValueType.of(String.class));
After adding the environment discrimination process
SessionProvider sessionProvider = System.getenv(APP_HOME_DIR) == null ? new LocalSessionProvider() : new RemoteSessionProvider(CACHE_URL);
Session cacheSession = new RemoteSessionProvider(CACHE_URL).createSession(Transport.rest());
Cache cache = cacheSession.getCache(CACHE_NAME, ValueType.of(String.class));
The SessionProvider is switched depending on the presence or absence of environment variables.
Example of executing Application Cache in the local environment
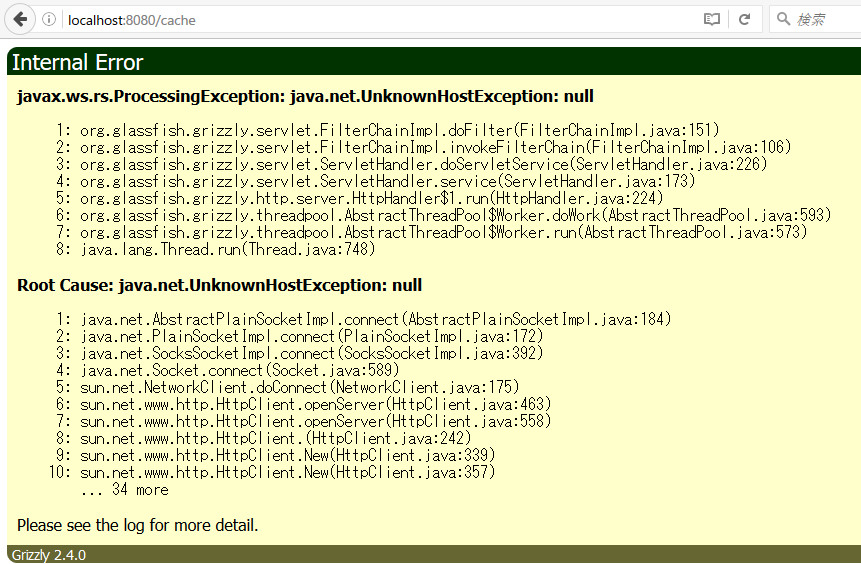
Local access when using RestCache
Local access when using LocalCache
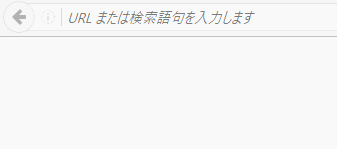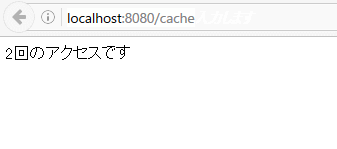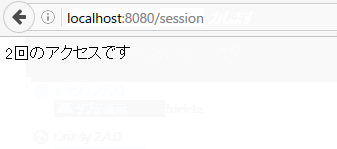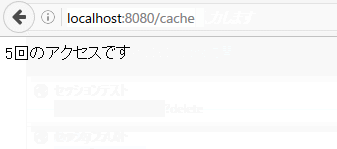
Summary
Until I noticed the existence of LocalCache, I was wondering if I would pull out the host name where Application Cache is running from the environment and develop it while connecting remotely. LocalCache helps you because you don't have to worry about remote connections during development.
Recommended Posts